FOOD CONSERVATION AND FREEZING DIVISION
The speed of most chemical, biochemical and microbiological reactions depends on the temperature. As the temperature decreases, the reaction rate decreases. As the alteration is usually a consequence of chemical reactions mediated by endogenous microbes and enzymes (present in food), the shelf life of some foods can be prolonged through storage at low temperatures.
Currently, cooling and freezing are the technologies that have the greatest importance in the food industry.
Industrial food freezing is generally divided into three large groups of frozen foods, classified according to the thermal transmission medium:
- Direct contact (Generally immersion)
- Air recirculation
- Cryogenic process
In these systems, the food puts in contact with a plate, a liquid or a metal band from which the thermal transmission by conduction will be carried out (contact between solids). These devices ensure a short freezing time provided that the product is a good heat transmitter and its thickness is not excessive (less than 50-60 mm). It is very important that throughout the freezing process a close contact is maintained between the product and the freezing surface. Three types of freezers are distinguished by direct contact: of plates, bands and rotating drum.
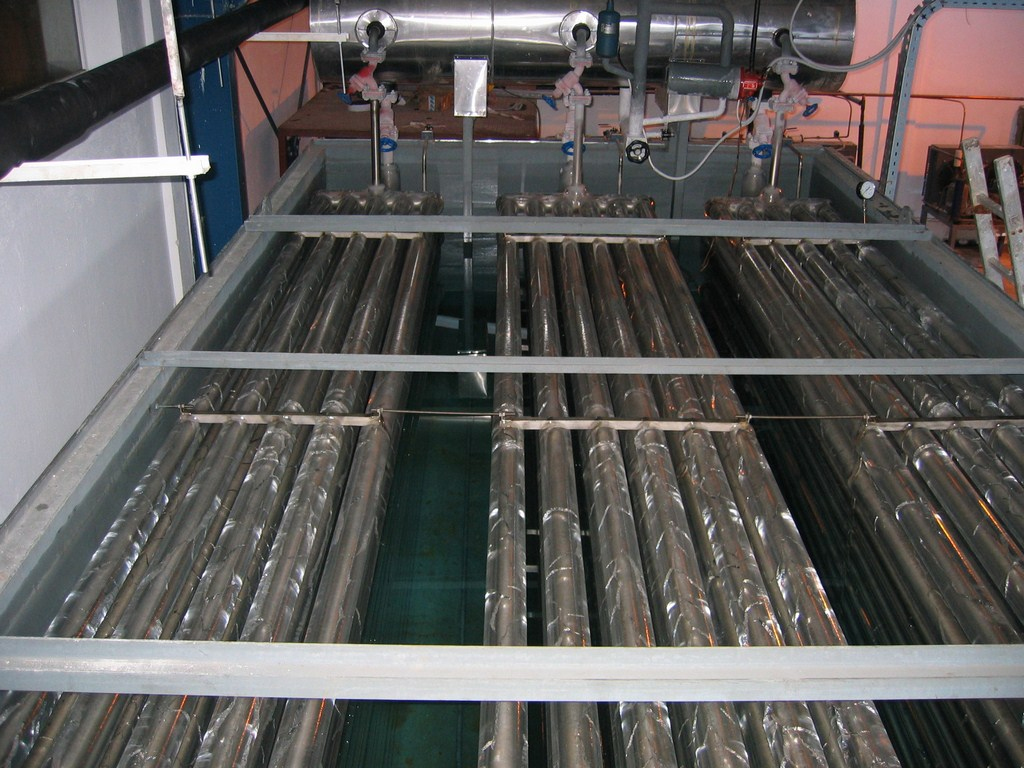

Air is the most common freezing system.
It should be made clear that a frozen preservation chamber should not be considered a freezing system. The freezing rates achieved in the chamber are very small, so the quality of the products obtained will always be low.
Air freezing in good conditions is carried out in equipment specially designed for this purpose, such as freezing tunnels, conveyor belt freezers and fluidized bed freezers. In all cases, evaporators are used through which a cooling medium circulates (such as ammonia), the air passes through the evaporators, cools and in this way passes through the product, carrying out the phenomenon of freezing.
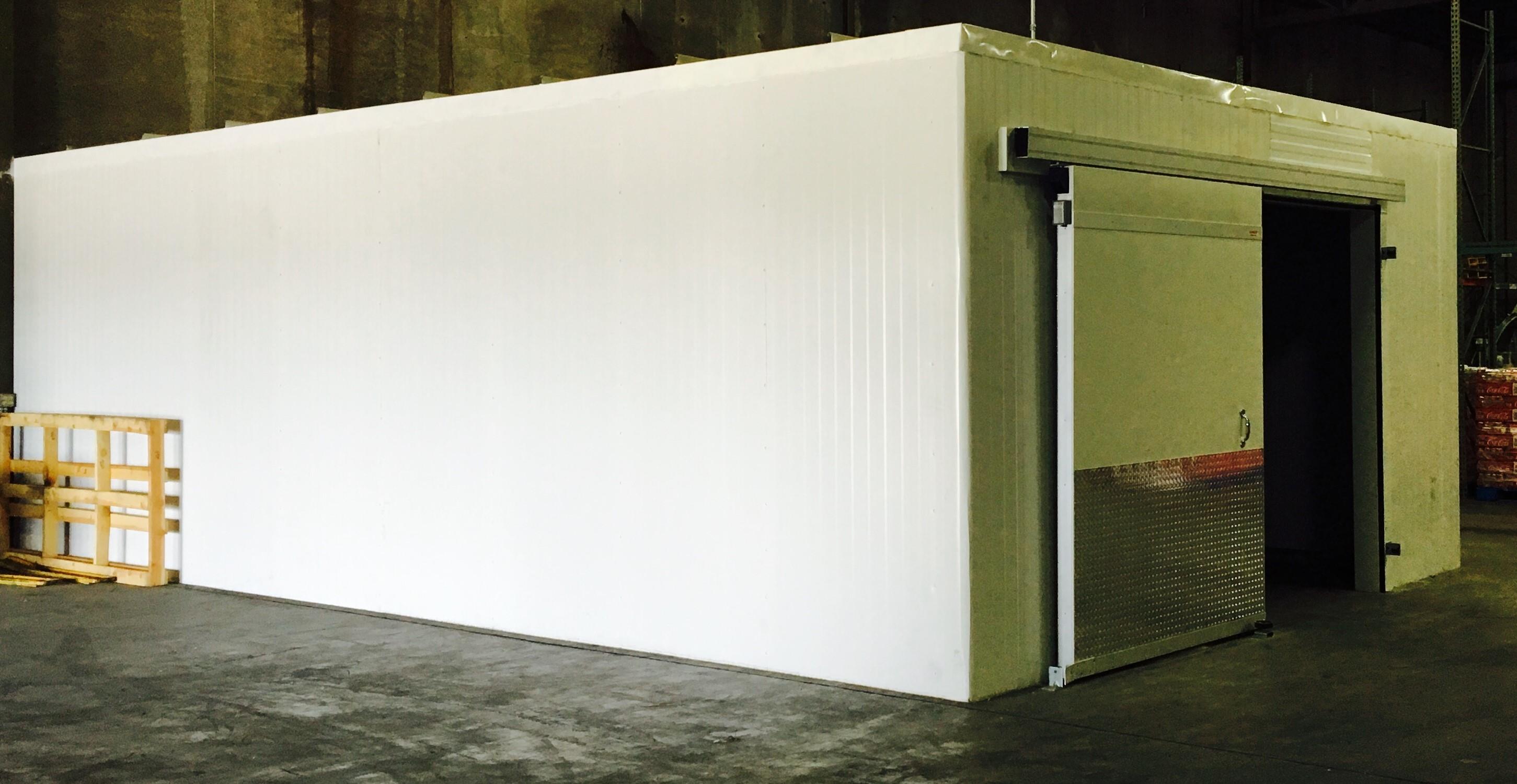

These systems do not need to be connected to a mechanical cold production system. The heat transfer medium is generally liquid nitrogen, stored in the vicinity of the equipment.
The cryogenic alternative offers maximum advantages for small capacity installations or for the initial production of new products, since its high operating costs will not allow its use for most products.
Liquid nitrogen freezers can be found that work by immersion or by spraying the cryogenic liquid.

STRATEGIC ALLIANCES




Development and validation of thermal processes

Food Security and Safety

Evaluation of funding sources to land the necessary resources
Personalized training, according to the production process to be carried out

Process authority

Entity training and evaluator of operating conditions prior to the FDA visit

Development and implementation of quality systems

Development and management of federal inspection type certification

Integration to the value chain, linking it, according to the stage in which the process is

Development of business model oriented to objective markets, potentializing opportunities and mitigating risks

